The Fulani (also known as Fula or Peul) are a pastoralist people who have long been a significant presence across West and Central Africa. With a rich culture and history, the Fulani have played a major role in the development of many African nations, including Nigeria, Mali, Senegal, Guinea, and Cameroon.
The Fulani are traditionally nomadic herders, moving their cattle, sheep, and goats across the grasslands of West Africa in search of pasture.
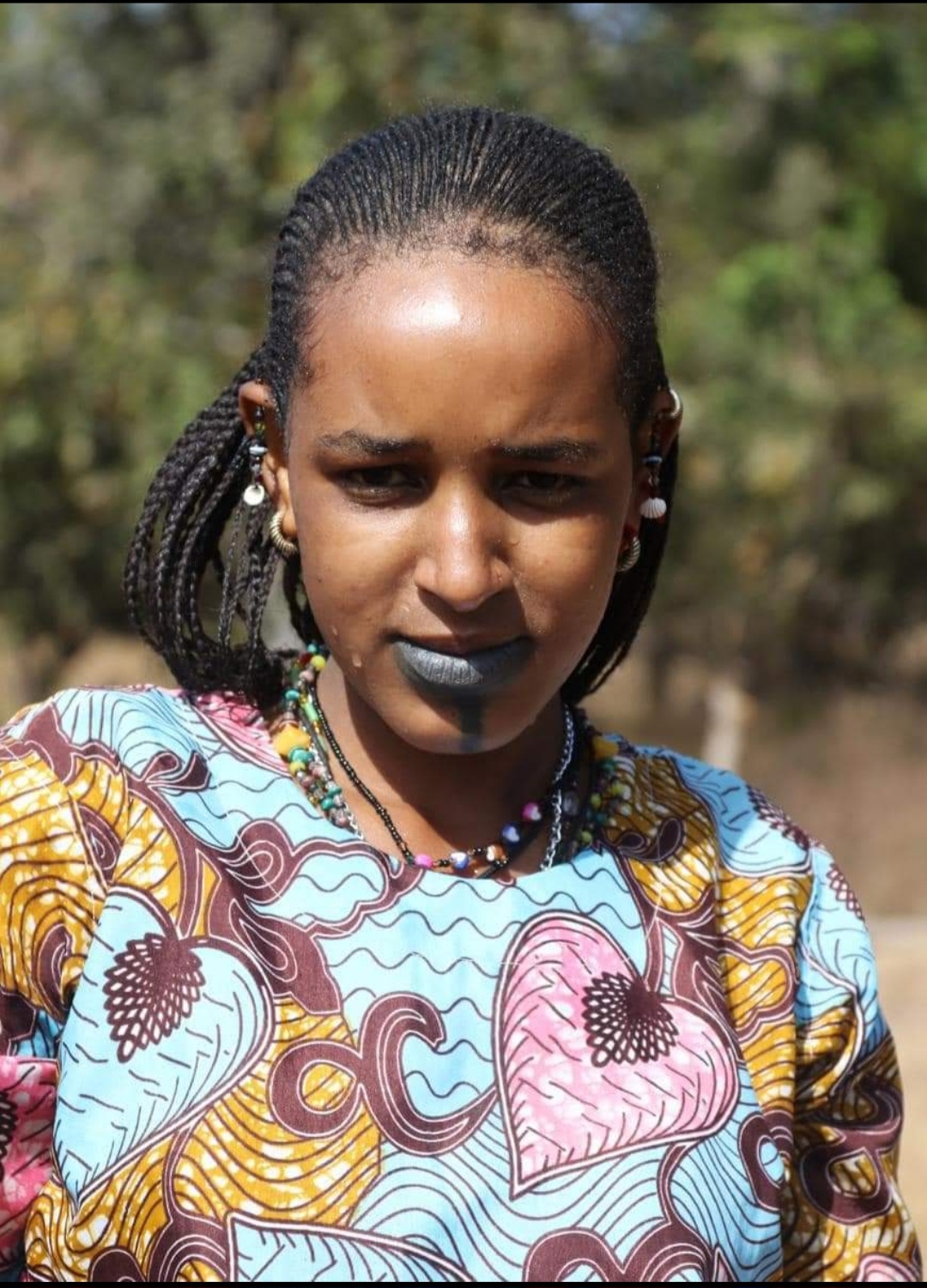
The Fulani have a rich and unique culture that is centered around their pastoralist lifestyle and their Islamic faith. They speak Fula, a language related to the other languages of West Africa, and many also speak French, English, or other local languages.
The Fulani are known for their distinctive clothing, with men often wearing long robes and turbans, while women wear colorful, patterned dresses. They are also known for their unique styles of jewelry, including large hoop earrings and bracelets made of leather and metal.
The Fulani are also known for their music, which features traditional instruments such as the lute-like hoddu, the goje (a one-stringed fiddle), and various types of drums. Fulani music is often used to celebrate important events and ceremonies, such as weddings and naming ceremonies.
Despite their nomadic lifestyle, the Fulani have a strong sense of identity and culture, with a deep respect for their traditions and their connection to the land.
The Fulani are a vibrant and dynamic people, with a rich history and culture that has shaped the fabric of West and Central Africa. Their nomadic lifestyle, their Islamic faith, and their unique cultural traditions have made them a distinctive and influential force in the region, despite the many challenges they have faced. Today, the Fulani continue to preserve their way of life and their cultural heritage, while adapting to the changing world around them.










0 Comments